Insulation R-Value
When installing insulation, the most important thing to pay attention to is its R-Value. Most people know that the higher an R-Value's number, the better it will be at its job. But what exactly is an R-Value?
R-Value - What Is That?
Insulation R-Value is a measure of thermal resistance. It is used in home construction to define the efficiency of installed insulation. You can think of it as a blanket on your bed on a cold winter's night; the thicker the blanket, the warmer you'll be. Insulation works in much the same way to keep your home comfortable year round.
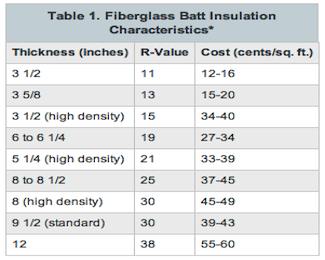
The insulation R-Value will depend on its material, thickness, and density. Installing more insulation to your home increases the overall R-Value, and thermal resistance to heat flow.
The Higher The Insulation R-Value, The Better
The R-Value of any insulation product is listed as a number; the higher the number, the better the insulation will be at reducing thermal resistance.
How and where insulation is installed in the home will determine its effectiveness. Proper installation is critical for insulation to achieve its full R-Value. Manufacturer R-Values on their product will apply ONLY to Insulation that is installed correctly. Insulation that is compressed will perform at a lower R-Value
To Compact Or Not To Compact
For example, adding twice the amount of insulation may double its R-Value, but if you are squishing it down to fit twice the amount in the same amount of space, the R-Value will increase but not double. Improperly installed insulation around edges, studs, and joists will leave gaps or other spaces that will allow heat to leak through, greatly reducing the R-Value.
It's also important to consider that even insulation that has been installed correctly will not reduce heat flow in areas such as windows, doors, and uninsulated wall studs. The R-Value of insulation is only one piece of the larger puzzle that is a super-efficient green home.
How Much Insulation Should You Add?
The amount of insulation, and its accompanying R-Value, a home needs to be really efficient depends on the climate zone its built in.
Homes in areas that experience extreme heat or cold will obviously benefit from insulation with higher R-Values. Different parts of the home will also require different R-Values due to the nature of hot air; it rises, so therefore more insulation with higher R-Values are typically used in attic spaces.
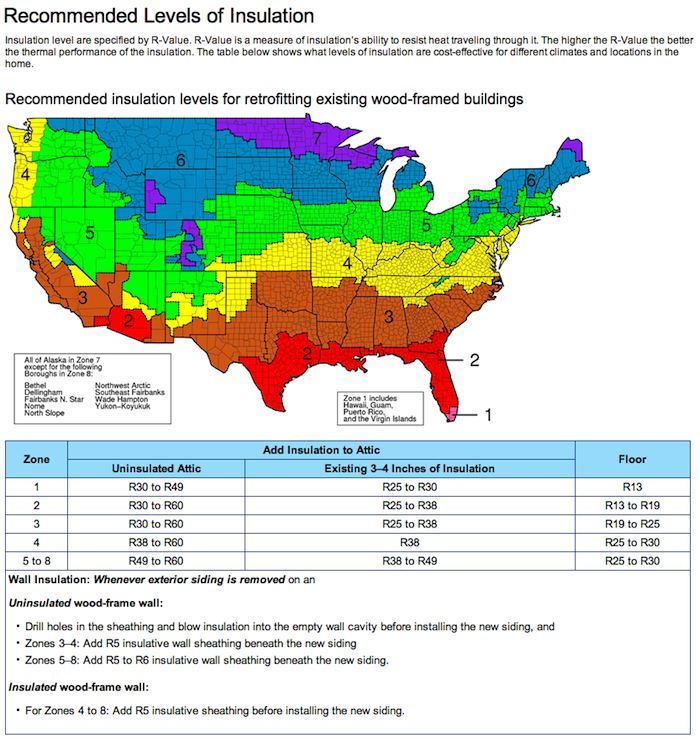
The Department of Energy has recommended R-Values for areas around the U.S. based on local energy costs, as well as the average local climate. There are different types of insulation available for homes, such as roll (or batt), loose-fill, rigid foam, or spray foam. Each have varying levels of R-Value as well as their own advantages and disadvantages. The insulation you choose for your own home depends largely on how efficient you want your home to be while staying within a personal budget, and what type of climate it's located in.
This chart from Energy Star shows how much insulation is cost-effective for homes in your area:
For more information on the different types of home insulation, see our articles here.
comments powered by Disqus