Energy Efficient Windows

Energy Efficient Windows - Andersen 400 Series
Until quite recently, a home's windows were one of the biggest sources of energy loss in the entire structure. Over the last few decades however, major advances in window technology have largely rectified this; since the early 1980s, the energy performance of a typical window has been improved by over 50%.
Doing some research into the windows you select for your home can save a great deal of energy (and money!) over the lifetime of your house. There are a lot of window companies and choices out there, all promising energy savings. What are some of the things to look for when shopping for windows?
Energy-Efficient Windows: Multiple Panes
Many older homes still have original windows with only one single pane of glass. Today's windows have double-paned glass to increase the window's efficiency. The space between the panes acts as a thermal barrier between the indoors and outdoors. More expensive windows can contain triple-paned glass to increase efficiency even further.
Energy-Efficient Windows: Low-E Glass

The use of low-e glass can greatly increase the r-value of new windows. Low-e glass contains invisible layers of special coatings, typically tin dioxides or thin silver layers. These coatings reflect radiant energy, keeping that heat on the same side of the glass from which it originated, while still letting visible light pass.
During hot periods, the heat (and UV rays) of the sun is reflected away, lowering cooling costs. On the flip side, during cooler months, the low-e window keeps heated air on the inside of the house, lowering heating costs.
The premium price of low-e windows, usually 10-20% higher than traditional windows, will pay for itself in just a few years in energy savings.
Energy-Efficient Windows: Fill 'em Up with Gas
Many efficient windows today inject an inert, low-conductivity gas in the space between layers of glazing to greatly improve thermal performance. Most use argon gas, though some ultra high-efficiency windows use krypton or a mix of argon and krypton between the glazing layers.
Energy-Efficient Windows: Frames Are Important, Too
The material used for a window's frame can also improve it's efficiency. Vinyl frames have a good thermal performance, but can be prone to warping and sagging. Weather sealing can also be a problem with low-quality vinyl windows due to the expansion and contraction of the vinyl plastic from temperature variations.
Other efficient window frame materials include fiberglass with foam insulation and composites made from recycled plastic and wood. The 'original' window framing material, wood, is still the best for energy efficiency. Many manufacturers add vinyl cladding to a wood window's exterior side for lower maintenance.
Energy Star Windows
A great way to start your search for windows is to simply look for the Energy Star label. Energy Star was established by the U.S. government to effectively measure and rate home products, and make it easier for consumers to identify energy-efficient products that offer savings on energy bills without sacrificing performance.
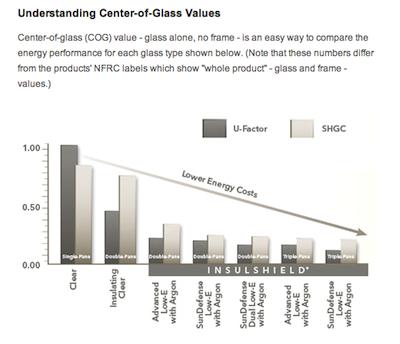
Pella Windows - Center-Of-Glass Insulation Values
An Energy Star product will save energy and money, and also reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants caused by the inefficient use of energy. Energy Star approved windows are certified to:
- Save Money: A typical home with Energy Star windows installed can save an average of $71-$247 per year over regular double-pane glass, keeping anywhere from 692 to 2,825 pounds of CO2 out of the atmosphere,depending on the home's location. That's the equivalent of 35 to 144 gallons of gasoline. When comparing Energy Star windows to single pane windows, the savings are even greater: from $146 to $501 per year, from 1,147 to 3,839 pounds of CO2 reduction, which is equivalent to 59 to 196 gallons of gasoline!
- Increase Comfort Levels: Efficient, Energy Star windows do more than save energy and money; they make your home more comfortable year round. Efficient windows are more comfortable to be around in cold or hot weather. In the winter, inefficient windows have cold inside surfaces, pulling heat away from your body. Efficient windows stay warmer. In the hot summer months, inefficient windows can allow 75% of more of the sun's heat into your home. Efficient Energy Star windows reduce this heat gain, allowing the inside glass to remain much cooler.
- Reduce UV Damage and Fading: Windows without a low-e coating allow a great deal of the sun's UV rays into the home. This can lead to fading of drapes, wood floors, photographs, and furniture. Efficient, Energy Star windows act like a sunscreen for your home, keeping UV light out without reducing visible light. The coatings on efficient windows can reducing fading by 75% or more.
Energy-Efficient Windows and Green Home Source
All green home plans designed by Green Home Source specifically call for efficient windows certified by Energy Star and The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC). These ratings provide a useful tool when comparing and choosing windows for your home and will ensure that your home is as energy-efficient as possible.
comments powered by Disqus